Content:
When growing cultivated plants, it is important to observe crop rotation. Some plants impoverish the earth, others enrich it with nutrients. To maintain soil fertility, it is not necessary to apply chemical fertilizers. Plants can also cope with this function. The main thing is to choose the right green "helpers". So, legumes add nitrogenous compounds to the soil. That is why they are the best predecessors for other cultures.
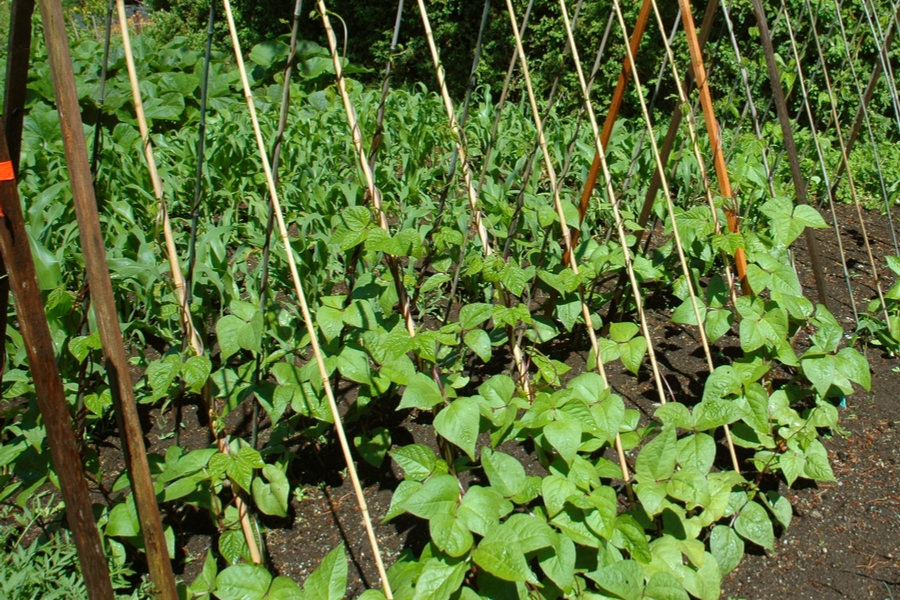
Conditions for growing beans
The beans can grow in all conditions. But in order to obtain a large harvest, the choice of a place for planting them should be approached thoughtfully.
Loamy and clayey soils are better suited. They love moisture, but cannot stand its stagnation. They respond positively to the introduction of manure before planting. This crop does not grow on sandy and acidic soils. It is best to grow beans in a bright, open area. For better development, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are applied before planting seeds in the beds.
Due to the fact that legumes do not grow on acidic soils, in the fall the beds for this species are limed by adding 300-400 gr. lime per square meter. The prepared bed in the spring is treated with a solution of trichodermine to prevent fungal diseases. Before planting, the seeds are mixed with nitragin to increase yields.
These vegetables are not afraid of frost. Seeds germinate at a temperature of +4 C. They tolerate heat worse. The substrate in the plant well must always be moist. For growth, they need a temperature of + 17-18 C.
What is sideration and legumes-siderates
In crop production there is such a term - sideration. This term means growing plants with a large green mass and then plowing them into the topsoil to enrich the soil with organic matter and nitrogen. For this, mainly legumes are used - peas, lupine, sweet clover, clover and others.
All varieties of legumes not only enrich the soil with nitrogen, but also convert phosphorus into a form more accessible to other varieties. The rapid growth of green mass allows you to fertilize the soil with organic matter at no additional cost.
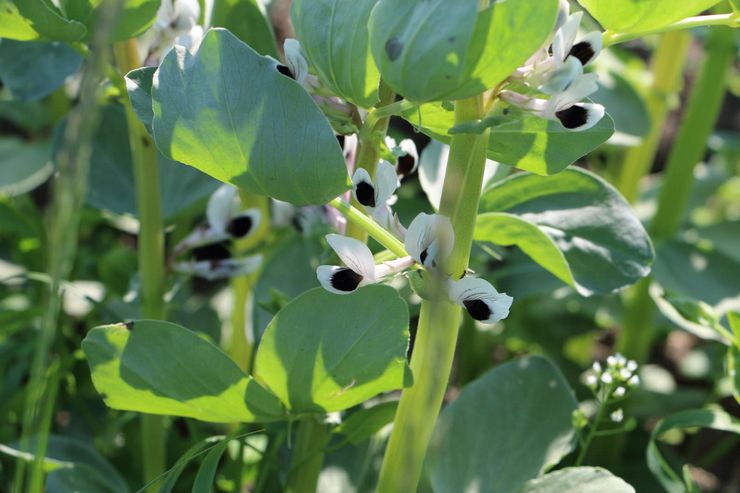
One of the best siderates are broad beans. These are annual plants that grow up to two meters. Withstand frosts down to -8 C and are less demanding for watering. During the growing season, they are able to assimilate and convert up to 300 kg / ha of nitrogen. After mowing the tops, half of this nitrogen remains in the soil and can be assimilated by other species.
The root system of legumes is pivotal and penetrates deep into the soil. Thanks to this, it becomes looser and saturated with oxygen, which increases its fertility. Leguminous plants reduce the acidity of the soil, contribute to the carbon nutrition of plants and improve the soil microflora.
In addition to improving the soil, this class of vegetables helps in the fight against harmful insects. They attract predatory insects such as the wasp wasp.In addition, some species release substances that are natural pesticides and fumigants.
All this makes this class the best predecessors for most cultures. However, each crop has its own predecessor in the garden to increase the yield. The table shows the legume precursors for major vegetable crops.
| Vegetables | Suitable predecessors |
|---|---|
| Eggplant, onion | Beans, beans, peas |
| Zucchini, cabbage, potatoes, carrots, cucumber, bell pepper, pumpkin | All legumes |
| Beet | Beans |
| Tomatoes | Beans, peas |
Beans: what to plant next to?
Novice gardeners tend to plant vegetables nearby in order to save space on the site, and sometimes in the same garden. But more often such a neighborhood does not bring the desired result. Some varieties support, while others oppress their neighbors. So what can you plant the beans with? To figure out for which plants beans are the best neighbors in the garden, the table will help.
| Vegetables | Bean neighbor |
|---|---|
| Carrots, cabbage | Peas |
| Basil, beets | Beans |
| Cabbage, cucumber | Beans, peas |
| Eggplant, beets | Beans |
| Pumpkin | Beans, beans, peas |
| Potatoes | Beans (perimeter), beans |
| Tomatoes | Beans, beans |
As a result of joint sowing, the surface layer of the soil is enriched with nitrogen and other nutrients, the germination of weeds and the risk of pest attacks are reduced.
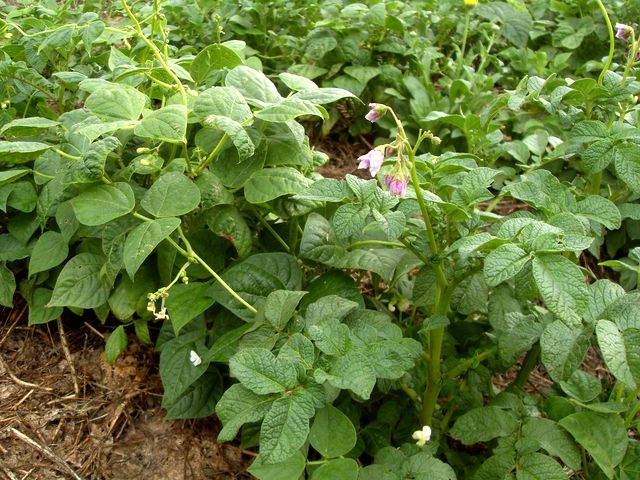
How to plant beans with potatoes
A common advice is to grow beans with potatoes. This cannot be done for the following reasons.
- seedlings of legumes grow faster than potatoes and this will darken the latter.
- potassium is important for potatoes. Beans also absorb large amounts of it and potatoes will miss it.
- due to bacteria-symbionts on the roots of leguminous potatoes, they will be infected with scab.
- with a combined planting, potato yield will fall.
How do you plant beans and potatoes? It is better to grow green manures around the perimeter of the potato field. They will create a barrier to the cold wind. In addition, in areas where potato plantings suffer from moles, such a protective strip will scare them away.
The Colorado potato beetle also doesn't like planting these vegetables in potatoes.
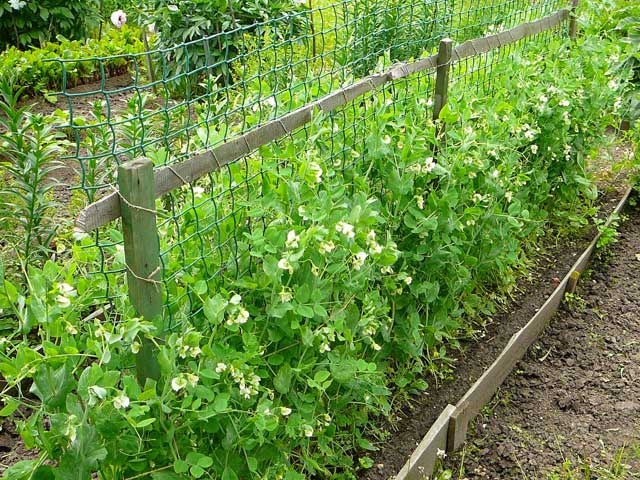
Is it possible to plant beans and peas nearby
Beans and peas belong to the same family. There are no obvious contraindications to sowing these crops together. It is possible to grow them nearby.
But, unlike beans, peas do not grow on clayey, acidic, very moist soils. He is afraid of frost, peas are sown at the end of May. The beans can be sown at the end of April. Potash and phosphorus fertilizers are important for nutrition of peas, but beans develop faster and peas will lack nutrients. In addition, the faster development of the beans will result in the drowning of the young pea sprouts. It is for these reasons that you should not plant peas and beans in the same bed.
The cultivation of beans, peas and beans on the site will not only allow you to get tasty and rich in protein and vitamins vegetables, but also significantly improve the soil on the site. These plants do not have to be sown in spring, they can be planted after harvesting the main crops specifically to enrich the land with nutrients. Around October, the green part of the plants is plowed into the soil and left until spring. Growing legumes both for nutrition and for improving the soil will give excellent yields for other crops.