Articles are called certain parts of the horse's body, each performing its own function. The statues are an important part of this animal's anatomy. It is important for everyone to know them. It will be interesting both for amateurs and for those who are planning to buy a horse soon. There are more than 60 articles. First you need to figure out where what is and what is called.
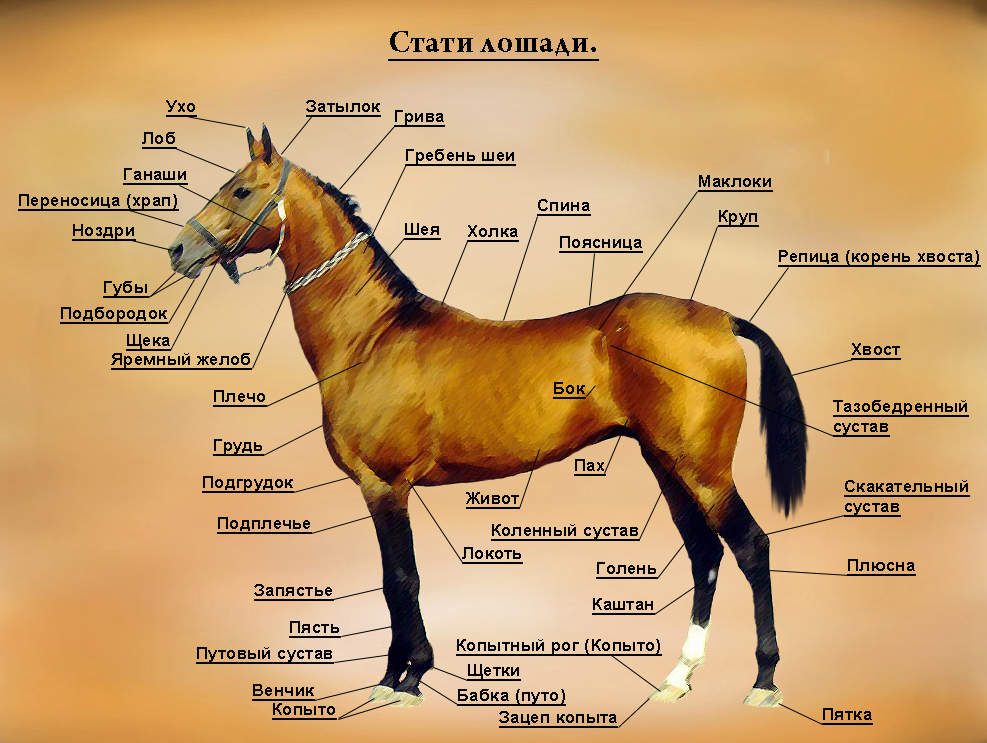
Main horse stats
The main horse head articles are:
- occipital crest,
- ears,
- bang,
- forehead,
- eyes,
- nose (snoring),
- nostrils,
- muzzle,
- lips,
- chin,
- chin fossa,
- branches of the lower jaw (between them there is a slap in the face),
- slap (ganache),
- nape,
- skull.
Next are the main neck stats. Among them are:
- crest of the neck,
- side of the neck,
- throat,
- jugular groove,
- withers.
These are followed by the statues of the animal's body. These include:
- shoulder-scapular tubercle,
- chest,
- back,
- chest (ribs),
- sternum,
- stomach,
- false ribs,
- sigh,
- small of the back,
- maklok,
- croup,
- tail tail,
- sciatic tubercle,
- sacrum,
- tail,
- prepuce.
The main limbs of a horse are:
- scapula,
- shoulder,
- forearm,
- wrist,
- pastern,
- fetlock,
- puto (at the same time has a second name "Babka"),
- whisk,
- hoof,
- elbow.
On the hind limbs are:
- hip,
- knee,
- shin,
- heel,
- pastern,
- hock joint of the metatarsus,
- fetlock,
- bristles and spurs,
- puto (grandma),
- whisk,
- hoof,
- chestnuts,
- hoof heel,
- buttock.
Horse articles rating
Now you need to take a closer look at each article. First of all, you should examine the head of the animal. Experts say that a large head disfigures a thoroughbred horse, moreover, because of a large head, there is a great load on the forelimbs of the animal. At the same time, the small head is also a disadvantage. When evaluating a horse's head, experts look at the dimensions of the distance between the ramifications of the lower jaw.
Horse ganaches (cheeks) should be at a distance of 8-9 cm from each other. With this indicator, the breath of the horse in harness is not constrained. In addition, the head, like the neck, is the regulator of the animal's center of gravity.
When evaluating a horse's muzzle, attention is primarily paid to the shape. The muzzle of a horse in profile is straight, concave and convex. The skull of a horse consists of 34 bones. The bones of the skull are very strong because the vital organs are located in the skull.
The nostrils should be clear and flexible. Pallor and redness of the nasal mucosa can warn of a horse's illness. Lips - not damaged. Also, the upper lip should be mobile, there is a labial groove on it. The chin is located under the lower lip.
The eyes must be clean and healthy (no cloudiness or various spots). The shape and size of the eyes are also taken into account when evaluating. In most horses, the pupil and iris are dark in color (brown or black). The blind spot is in front of the nose and behind the croup.
The ears must meet the standard requirements that are prescribed for the respective horse breed. There are three types of ears: pointed, straight and rounded. Also, experts pay attention to the mobility of the ears: if the ears are completely immobile, then this may indicate that the animal may have deafness. If the horse moves its ears excessively, then this can also indicate problems, but already with vision.
The teeth of a horse are of particular importance when evaluating articles. It is by the teeth that the age of the horse is determined.The incisors change most with age, but you can also determine how old a horse is by the wear of the teeth. In the first two weeks of life, milk hooks are cut through. The middle incisors are added to the month, and the extreme ones grow in the seventh month of life. By one year, the toes and middle incisors begin to wear off, and by the age of two, the cups are erased at the extreme.
By the age of two and a half, all milk teeth fall out and are replaced by permanent ones by the age of five. On the lower toes, the calyx is erased in 6 years, on the middle incisors in 7 years, and in the extreme ones by 8 years. On the upper teeth, the cups wear off a little more slowly, usually in 9 years on the toes, about 10 years on the middle incisors, and 11 years are required for the surfaces to wear off on the extreme incisors. Horse teeth should be examined frequently to prevent various diseases.
The neck is judged by the shape of the position relative to the trunk. It can be high, normal and low. The length and width of the neck depends on the breed of the horse. Horses are characterized by a long and thin neck, while heavy draft horses are wide and short.
The withers are scored for height, length and width. For riding horses, it should be high and long, and for heavy draft horses, it should be low and wide. The height of a horse at the withers depends primarily on the breed. The height of the horse varies from 70 to 200 cm. High withers appear during training.
The back is scored for length, width and shape. The latter can be straight, soft, sagging, carp-like. All horses are characterized by a broad, straight and muscular back. If the back is saggy, then this is a designation that the horse has had a lower back injury.
The loin is scored for length, width and shape. The shape is straight, convex, carp-like and sunken. In all horses it should be broad, straight and muscular.
The croup of a horse is assessed in terms of length (not less than 35% of the body), width, slope (straight, normal, drooping), shape (round or oval, roof-like, bifurcated) and musculature.
The horse's chest is scored for length, volume, width and depth. A large chest volume is best for horses.
The tail can be set high or low set. It is located at the end of the croup. It is important to know that in no case should the cauda equina and simply the tail be confused, since the cauda equina is the second name for the horse's spinal cord. When assessing the limbs, much attention is paid to the degree of development of the femurs. They should be oblong and have prominent muscles.
The scapula is scored for length and slope. She can be steep, oblique and mid-range. All horses have a long and oblique shoulder blade.
The elbow is judged by position relative to the chest. An elbow protruding to one side indicates poorly developed musculature of the shoulder, which can lead to injury to the animal.
The wrist is scored for width and length. It consists of seven bones in two rows. Thanks to this, it is very strong and allows you to bend the horse's limb well. The animal is characterized by a wide and long wrist.
The metacarpus is assessed for the length, shape and extent of the tendons. The thickness of the metacarpus indicates a strong bone structure.
The ropes (headstock) perform the function of a springy mechanism, taking on the entire weight of the body and transferring it to the hoof. They should be at an angle of sixty degrees, then the step will be soft and calm. If the restraints are straight and short, the horse's move will be stiff.
The tail joint should be well developed, wide, well defined and dry.
The hock joint is assessed by the angle of the joint and the distance between them. The angle of the hock joint should be about 150 degrees.
The hoof consists of a shoe, a dermal base and a subcutaneous layer. Damage to it can lead to lameness as well as impairment of horse performance.
A horse's rim is the top edge of the hoof.
Horse coloring primarily depends on the breed. The most common are bay, red and black.
Diseases of the hind limbs are: strongly set back hind legs, saber set, x-shaped, as well as o-shaped hind limbs of the animal.
The horses are hatched to be shown to the audience. Most often, the brood is found at exhibitions, at auctions, and also when participating in competitions. At the time of this, the animal should not have any ammunition, except for the bridle.
Show jumping horses also need various exercises. Such as: a football row or an obstacle in pace. There are also many other exercises for the show jumping horse.
Horse conformation assessment
The exterior helps determine the horse's breed and health status.
Experts rely on five aspects to evaluate a horse's conformation:
- Balance the horse's body. The proportionality of different parts of the body is taken into account. With the right balance, the horse is more agile, more powerful and smoother.
- Structural correctness. It is determined by the structure of the skeleton and its evenness. For the most part, structural correctness relates to the structure of the horse's legs. Since, to a greater extent, the performance of an animal depends on the development and condition of the limbs.
- Horse movement. They are rated for frequency and quality.
- Musculature. It is no longer as important as the above criteria. But the musculature is still subject to mandatory assessment of the structure of the horse. When assessing the musculature, first of all, attention is paid to its quality and the location of the muscles on the body of the animal.
- Breed and sexual type. When assessing it, experts find out how well the breed and sex characteristics of the animal are expressed. Therefore, it turns out how close the horse is to the ideal of its breed. Also, with the help of it, they are selected for breeding.
This text is important not only for those who are planning to get a horse in the near future, go to study as a veterinarian or start practicing equestrian sports, but also just for general development.